Cord Blood Stem Cells Storage in Thailand: The Ultimate 2024 Review

What are stem cells?
Stem cells are the body’s raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. These daughter cells become either new stem cells or specialized cells with specific functions, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells, or bone cells. No other cell in the body has the natural ability to generate new cell types.
Why is there such an interest in stem cells?
Stem cells can be guided into becoming specialized cells that can be used in people to repair tissues or regenerate particular parts of your body that have been affected by a disease. Currently, stem cell therapies are established for blood cancer treatments, but they are now also used to treat all sorts of diseases, including spinal cord injuries, cerebral palsy, type 1 diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, heart diseases, brain injuries, osteoarthritis, and in many other areas.
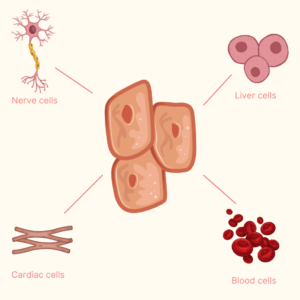
Types of stem cells: which ones are the best?
Human stem cells can come from any living cell. However, as stem cells age and specialize, their ability to change and turn into other cells deteriorates. This is why cells from an embryo are way more potent than stem cells collected from an adult. The most potent stem cells are called omnipotent and are derived from the fertilized eggs from in vitro fertilization. The second most potent stem cells are called pluripotent and can come from an embryo or cord blood. There are 3 main sources of stem cells used in therapies:
- Embryonic stem cells come from embryos that are 3 to 5 days old. At this stage, an embryo is called a blastocyst — an organism that contains about 50-150 cells. The good thing about embryonic stem cells is that they are omnipotent. But the problem is that to take them, you end up destroying the embryo.
- Stem cells also come from cord blood, cord tissue, and the amniotic fluid, all of which are also pluripotent. Like embryonic stem cells, they can divide into more stem cells, which can become any type of cell in the body. Since taking cord blood stem cells doesn’t harm the baby, they became more popular.
- Stem cells from bone marrow. When stem cells are not collected right after birth they can be collected from bone marrow. Compared with cord blood stem cells, collecting stem cells from bone marrow is more complex and can be painful. It is mostly done with adults, a time at which the stem cells might have lost some of their potency.
Note: Stem cells from cord blood, bone marrow, and peripheral blood are hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). HSCs are especially useful for treating the immune system and blood-related diseases. Cord tissue contains mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). MSCs cannot replace cord blood in bone marrow transplants but can be used for regenerative, cosmetic, and aesthetic purposes — for example, in the treatment of degenerative joint diseases like osteoarthritis.
Why do parents save their children’s cord blood?
Deciding to save cord blood is a personal decision. Some parents do it because the cells in cord blood are a perfect match for that baby and could be used to treat him or her for any serious health condition, like an immune system disorder or a problem with metabolism. Some industry experts believe that the chance that a child will need his or her own cord blood stem cells is about 1 in 2,700. This number is still relatively low, but with the advancements in science, it could go up significantly.
Have stem cells already been used to treat actual diseases?
For over 30 years, stem cell transplantations have been used to treat people with conditions such as leukemia and lymphoma. Relatively recently, stem cells are being used to treat many other conditions.
Here are some of the highlights of the last 30 years:
- 1988: The first successful cord blood transplant (CBT) was done in 1988 in a French child suffering from the blood disorder “Fanconi’s Anemia.
- 2002: Researchers successfully transplant stem cells into damaged eyes to restore vision.
- 2012: Stem cell therapy gets used for the management of graft-vs-host disease in children.
- 2020: Stem cell therapy shows promising results for patients with severe spinal cord injury.
- 2021: FDA approved the first clinical trial for a stem cell therapy to restore lost brain cells in people with advanced Parkinson’s disease
- 2022: Blood cord stem cell treatment helps cure a woman from HIV
Myth or not: Can cord-blood therapy treat autism?
According to results from the largest clinical trial to date of the therapy’s effectiveness for autism, there is little evidence to back cord-blood therapy for autism. The study, performed by a team from Duke University, had randomly assigned 180 autistic children aged 2 to 7 to either receive a single infusion of cord blood or a placebo. The results were published in May 2020 in The Journal of Pediatrics and showed that there is, unfortunately, very little scientific support for some claims that stem cells can be used to treat autism spectrum disorder.
Why are there so few actual cases of cord blood stem cells being used?
To date, only over 35,000 cord blood stem cell transplants have been performed worldwide. There are two main reasons why the number has not been much higher. The impossibility of finding a match. The latest record of public stem cell banks in Thailand in 2021 shows that for around 5,000 donors, there will be 1 match use case. Most children whose stem cells are being banked are still young, which means it’s very unlikely that they have had the need to use their cells for treating diseases that usually occur later in life. The technology is still very young, and more clinical research needs to be conducted. Many members of the medical community believe that many newer therapies may come to market in the near future.
Who can use my child’s cord blood stem cells?
- Cord blood stem cells cannot be used to treat your child’s genetic disease — a disease that your child is born with — because the cells carry the same genes that caused the disease in the first place. For that reason, your own child’s stem cells can’t be used to treat your child if he or she develops a certain type of leukemia. However, the cells can potentially be used to treat his or her other diseases or to treat a genetic disease of a biological “match”, such as a sibling.
- Donor stem cells always need to match the recipient. If there is no good match, the receiver’s immune system might think the stem cells are foreign invaders that want to attack the body. If that’s the case, the stem cells might fail to function, grow irregularly, or specialize in different cell types spontaneously. This means that people who don’t have access to a private bank or can’t use their privately banked cells, need to find matching stem cells via a network of public banks.
How are stem cells collected at birth?
Stem cell collection is quick and painless.
Collecting cord blood and cord tissue stem cells at birth:
After the baby is delivered, your doctor or healthcare provider will close off the umbilical cord using a clamp. Then, using a needle, the doctor will draw out the blood into a sterile bag. This will be sealed before the placenta is delivered. Sometimes the cord is simply tilted to let the blood drain into a bag. About ½-1 cup of stem cell-rich cord blood can be collected. If your plan includes the collection of cord tissue, the doctor will store that separately. All of this must be done within 15 minutes of birth.
Collecting placenta stem cells at birth:
If your plan includes the collection of stem cells from the placenta, this happens in a second step. Once the placenta is out, the placental tissue is divided and stored in bags. This can take up to 60 minutes.
What happens after the doctor collects the stem cells?
Once the stem cells are collected, the stem cell bank takes over. Their process involves freezing the cord blood and placenta tissue in a way that allows them to later be defrosted and suffused with a compound that enables the extraction of viable stem cells.
Note: Collection of the perinatal tissues at your child’s birth gives them the greatest possible volume of a broad spectrum of stem cells. As most private cord banks in Thailand pay the doctors in the hospital for the procedure and include these costs in their package, there should not be any additional costs for you for the procedure.
What’s the difference between cord blood and cord tissue cells?
The umbilical cord has two components: cord blood and cord tissue. Cord blood refers to the blood found within the umbilical cord and cord tissue actually refers to the umbilical cord itself. Cord blood and cord tissue are sources of at least two different types of stem cells, which is why some parents choose to preserve both cord blood and cord tissue.
The difference between HSCs and MSCs:
- Cord blood is an excellent source of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). HSCs produce all the cells in the blood. They are especially useful for treating the immune system and blood-related diseases.
- Cord tissue contains mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). MSCs cannot replace cord blood in bone marrow transplants but can be used for regenerative, cosmetic, and aesthetic purposes — for example, in the treatment of degenerative joint diseases like osteoarthritis or tendon injuries.
Note: HSC repopulates the bone marrow. If used in another setting, HSC will make blood vessels and the MSC in the HSC will perform regenerative functions. MSC on the other side, can only modulate inflammation and assist resident cells to do their job better.
How long can you bank stem cells?
According to the National Library of Medicine, collected stem cells can be stored for 21-23.5 years without a major loss in quality.
How far are the new therapies being developed with cord stem cells and blood cord tissues?
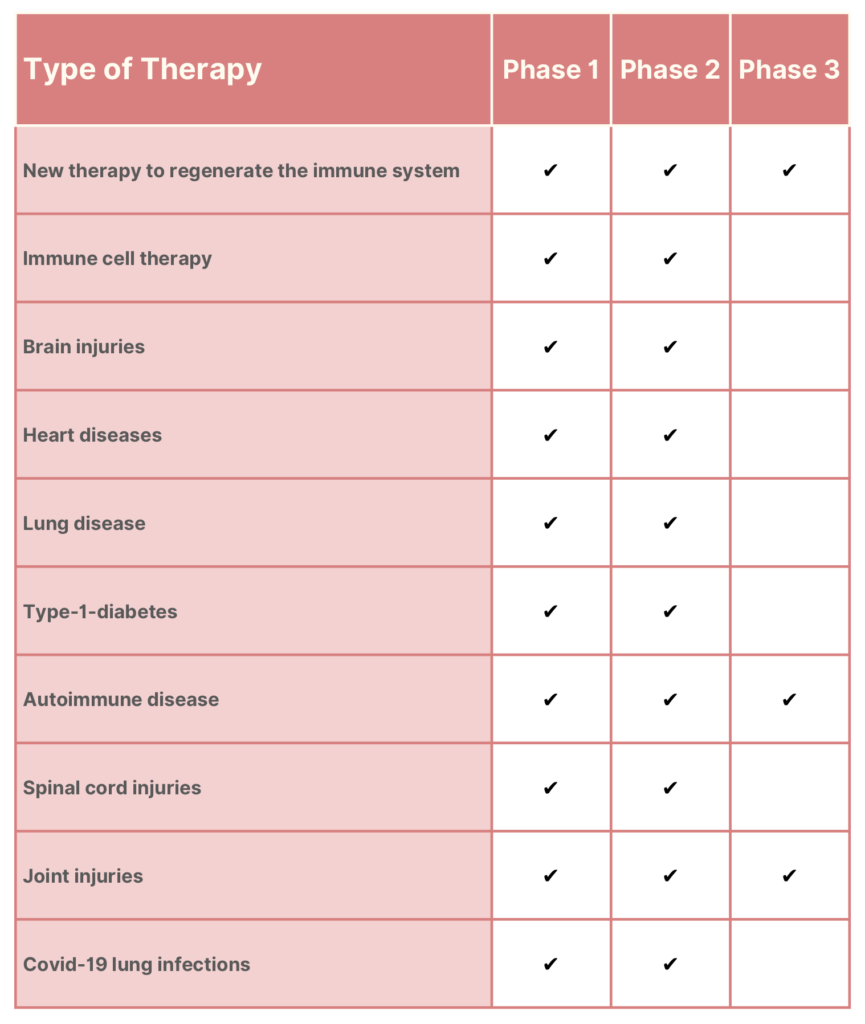
For any new drug or treatment to get FDA approval and be marketed as safe and effective, it must pass three out of the four phases of clinical trials — a process that can take years. See below for an overview of the different kinds of treatments for which cord blood stem cells and cord tissue stem cells are currently being tested.
Promising cord blood stem cell therapies in clinical trials:
Ways for storing cord blood: public and private banks in Thailand.

Public banks
Storing cord blood in a public bank is free. But the facility makes your stored cord blood available to other children who are biological matches. This means a public bank doesn’t store the blood of your child for your family’s use, but rather, for everybody. If the public bank network is large, the chances of finding a good match when you need it are high. If the public bank network is small, the chances of finding stem cells that suit members of your family are slim.
In Thailand, the Thai Red Cross established Thailand’s National Stem Cell Donor Registry (TSCDR) provides opportunities for stem cell transplantation. The Thai Red Cross also runs a Stem Cell Research and Development Committee, which includes the executives and specialists from Chulalongkorn Hospital, Siriraj Hospital, Ramathibodi Hospital, Phramongkutklao Hospital, and Songklanagarind Hospital.
Thailand’s National Stem Cell Donor Registry in numbers (estimates):
| Registered donors | 300,000 (31.12.2021) |
| People on the waiting list for stem cells | 200 (31.12.2021) |
| People treated with stem cells in 2021 | 60 |
| Total cases since 2002 | Leukemia: 250 cases |
| Thalassemia: 90 cases | |
| Myelodysplastic syndromes: 40 cases | |
| Aplastic anemia: 25 cases | |
| Lymphoma: 20 cases | |
| Age distribution | Most patients were 15 years or younger |
More details: https://stemcellthairedcross.nbc.in.th/en/about-us/tscdr-annual-report/
There are also other public agencies that do research on stem cells, such as the Siriraj Center of Excellence for Stem Cell Research, which is run by Siriraj Hospital.
Private banks
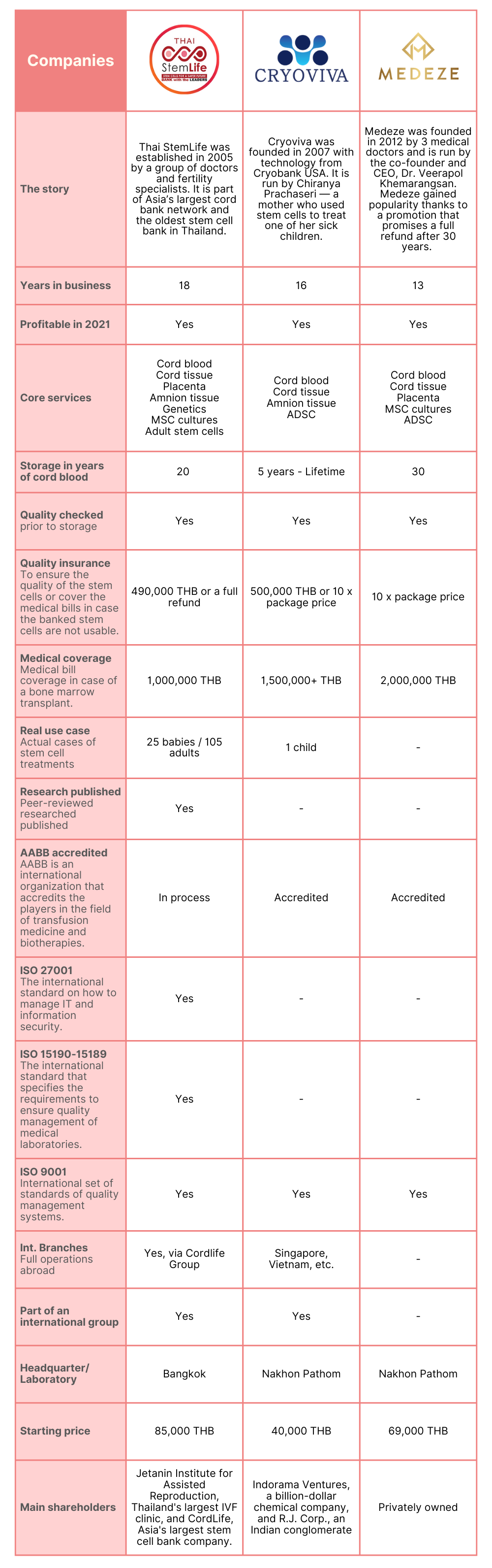
Storing cord blood in a private bank means that the cord blood will be available to your family only. This type of storage often requires an initial fee, storage fees, and a fee when the stem cells are to be collected for use. When storing at a private bank, it’s important to choose a facility that is trustworthy and well-funded so that it won’t be out of business when you need it. In Thailand, there are 3 major players in the market for cord blood banking.
Mali’s pick for 2024
Mali’s pick for 2024 is THAI StemLife because it’s the first and largest stem cell bank founded in Thailand, and also the only one with real life-saving cases. They are the only provider in Thailand that operates 24/7 for traumatic brain injury emergencies.
Sources:
- Are All Adult Stem Cells The Same?, Springer link.com
- Stem-cell therapy, Wikipedia
- Study finds little evidence to back cord-blood therapy for autism, Spectrum News
- Cord Blood Banking, Standford Medicine, Children's health.
- Stem cells: What they are and what they do, Mayo Clinic
- Embryonic stem cell, WikipediaStem cell treatment after spinal cord injury: The next steps, Mayo Clinic
- Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation, National Library of Medicine
- Manuel Neuer checked for doping, Bayern Munich News and CommentaryThe Thai Red Cross Society, Stem Cell Thai Red Cross
- "ธนาคารสเต็มเซลล์" ฝากชีวิตที่ดีเพื่อวันข้างหน้า, MGR Online
- Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, generation of induced pluripotent stem cells, and isolation of endothelial progenitors from 21- to 23.5-year cryopreserved cord blood, National Library of Medicine




